Benin
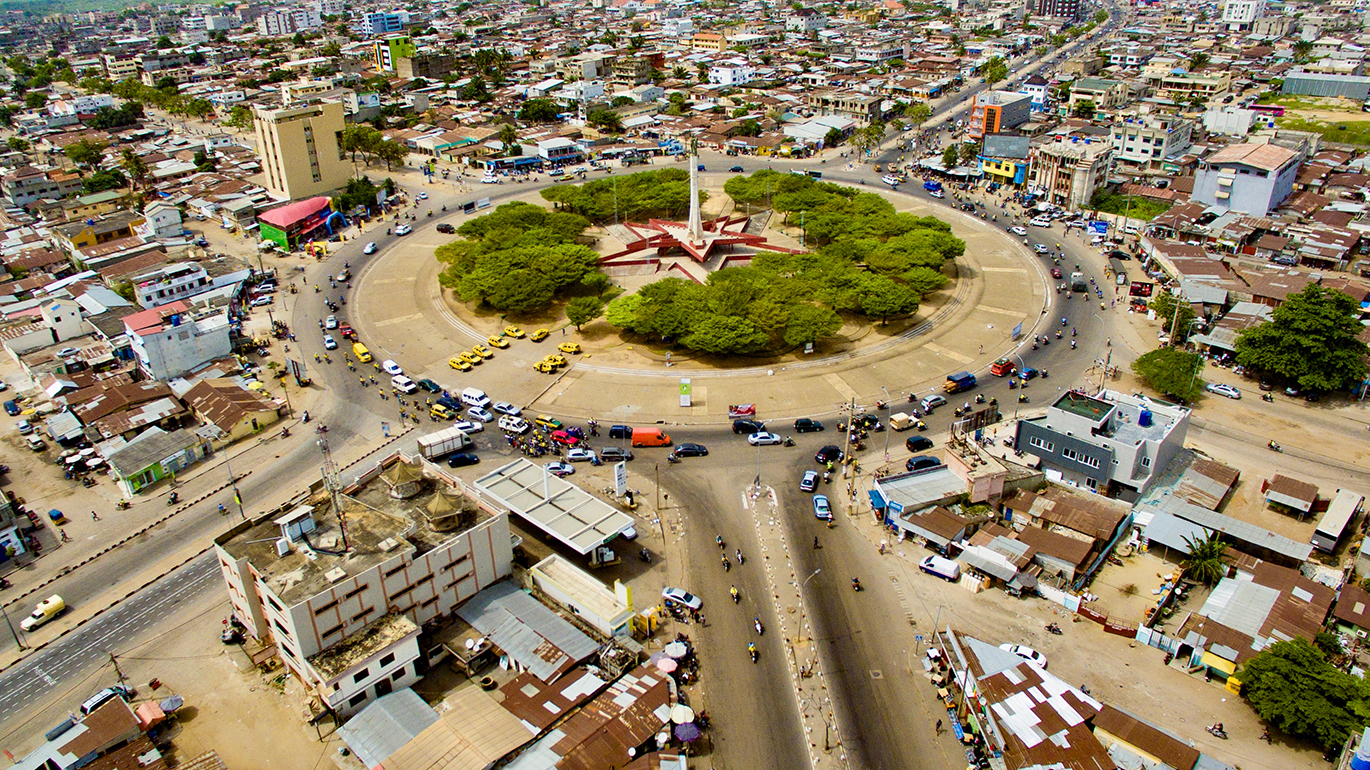
The modern state of Benin is bordered by Togo, Nigeria, Burkina Faso and Niger. The bulk of Benin’s population lives on the small southern coastline on the Bight of Benin, the stretch of water that gives the country its name.
Benin is a member of the CFA Franc Zone. French, the language of the former colonial power, has official status, though indigenous languages, such as Fon and Yoruba, are widely spoken.
Benin’s economy has grown substantially since the country transitioned to democracy in the early nineties. Growth is driven by agriculture and the country’s small commercial sector. Though cotton is farmed for export, most of the country’s population farm on a subsistence basis.
Benin drilled offshore oil for a period from 1982, though production has since ceased. Exploration of potential sites is ongoing, and the discovery of fresh oil reserves has the potential to invigorate the country’s economy.
The export sector is small, though growing. Key products include textiles and cashew nuts, mostly bound for Asia. Fish and shrimp are exported to Europe.
The economy has undergone privatisation in recent years, with formerly state-run enterprises passing into the hands of private companies – notably the formerly state-run brewery is now run by a French firm.
Benin is dependent on energy from neighbouring Ghana. The country has announced plans to develop a hydroelectric plant in conjunction with Togo in its drive towards energy self-sufficiency.
Our HLB West Africa team represents clients in Benin and is one of the region’s pre-eminent consultancy firms.
Featured insights
Latest insights, case studies and news from across the network